Edge Computing is a distributed computing paradigm in which processing and computation are performed mainly on classified device nodes known as smart devices or edge devices as opposed to processed in a centralized cloud environment or data centers. It helps to provide server resources, data analysis, and artificial intelligence to data collection sources and cyber-physical sources like smart sensors and actuators. Is edge computing seen as necessary? In the realization of physical computing, smart cities, computing, multimedia applications such as augmented reality and cloud gaming, and the Internet of Things (IoT). It is a way to streamline the movement of traffic from IoT devices and implement real-time local data analysis.
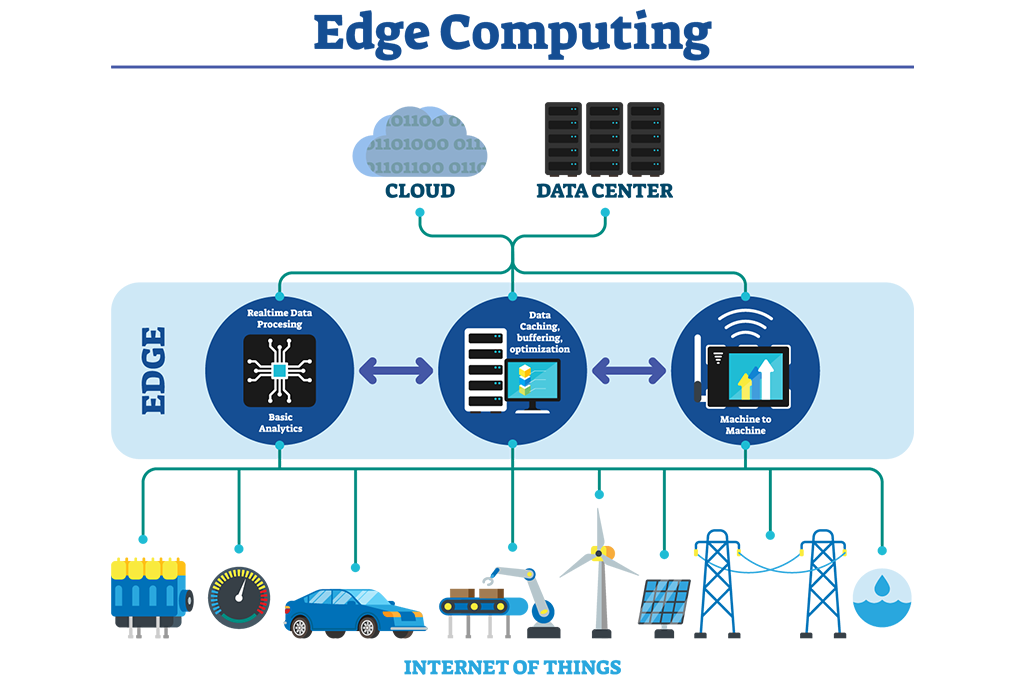
Data produced by the Internet of Things (IoT) devices to be processed where it is created instead of taking away to the routes to data centers with the help of edge computing. It also benefits Remote Office/Branch Office (ROBO) environments and organizations that have dispersed user base geographically. A significant benefit is that it improves time to action and reduces response time to milliseconds, while also conserving network resources.
“Practice of processing data near the edge of your network locally or on own server produced by IoT(Internet of Things) instead of centralized data processing warehouse. ”
Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing
In IoT, with the help of edge computing, intelligence moves to the edge. Like if you have massive amounts of data and for this, you have to leverage in such end to endways or highly sensor intensive or data-intensive environments where data is generated at the edge, which is due to IoT as data sensing at the edge.
And also, with real-time information, the increasing unstructured data of which sensor and IoT data are part, traditional approaches don’t meet the requirements which are needed. There are various scenarios where speed and high-speed data are the main components for management, power issues, analytics, and real-time need, etc. helps to process data with edge computing in IoT.
Benefits of Enabling Edge Computing for the Internet of Things (IoT)
- Lesser Network Load
- Zero Latency
- Reduced Data Exposure
- Computational Efficient
- Costs and Autonomous Operation
- Security and Privacy
Future Directions of Computing for the Internet of Things (IoT)
- Edge-to-Cloud data exchange capabilities
- Common-on-Edge data exchange capabilities
- Streaming Data Analytics and Batch frameworks and APIs
- Controlled rolling and Versioning upgrades of applications
- Status of application monitoring from an Ad-Hoc Cloud Dashboard
- Cloud-Based Deployments of Edge Computing Applications
- Edge-to-Cloud data exchange capabilities
- Common-on-Edge data exchange capabilities
- Streaming Data Analytics and Batch frameworks and APIs
- Controlled rolling and Versioning upgrades of applications
- Status of application monitoring from an Ad-Hoc Cloud Dashboard
- Cloud-Based Deployments of Edge Computing Applications
Why is Edge Computing Important?
- New Functionalities are offered.
- Easier configurations.
- Hacking Potential is increased.
- The load on the server is reduced.
- Load on Network is reduced.
- Application Programming Interface.
- Increases Extensibility.
- Centralized Management.
- Costs of Licensing.
- Support and Updates.
- Speed is increased.
- Reliability is increased.
- The random issue is reduced.
- The compliance issue is reduced.
- Hacking issues are reduced.
- Random issues are reduced.

 Recent
Recent Tags
Tags Popular
Popular







